News
New Epilepsy and Glutamate Excitotoxicity Assay
04 April, 2024
NeuroProof Systems GmbH has introduced two new assays for epilepsy and one for glutamate excitotoxicity. These new disease models have undergone rigorous validation and aim to support drug development projects effectively.
The 4-AP model focuses on the hippocampus, a key region in epilepsy, using primary hippocampal mouse cultures. It induces significant excitation in network cultures, as observed through increased spike and burst rates in MEA recordings.
The SCN1A assay showcases a new approach, utilizing adeno-associated virus constructs for transduction to create disease models in vitro. Knocking down the SCN1A gene in primary frontal cortex cultures from mice mimics features of Dravet Syndrome.
The glutamate excitotoxicity assay addresses a range of neurodegenerative diseases by inducing reliable hyperexcitation in cultured cells, which can be modulated with test compounds.
These new assays offer valuable tools for researchers in understanding and potentially treating neurological disorders.
TDP-43 Proteins in Axons of C9orf72 Mutations are Validating iPSC-Derived Motor Neurons as a Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
16 June, 2022
C9orf72 motor neurons exhibit TDP-43 condensates in somas and axons.
ALS pathology is only partially understood. TDP-43 proteins play an essential role in the mechanisms of this severe disease. Some evidence indicates that TDP-43 is an early marker of this disease starting from the neuromuscular junction.
NeuroProof investigated several markers of ALS in an automated imaging approach with the CQ1 system from Yokogawa in collaboration with Cenibra GmbH. In this study, TDP-43 was present in axons in C9orf72 spinal motor neurons, which is in concordance with other publications.
Phenotypic screening of human iPSC-derived motor neurons from patients with familial history is an excellent opportunity for screening new therapies for this severe disease.
NeuroProof has tested diseased ALS motor neurons with and without co-cultures of astrocytes in several screening assays besides its electrophysiological screening on its microelectrode array recording platform.
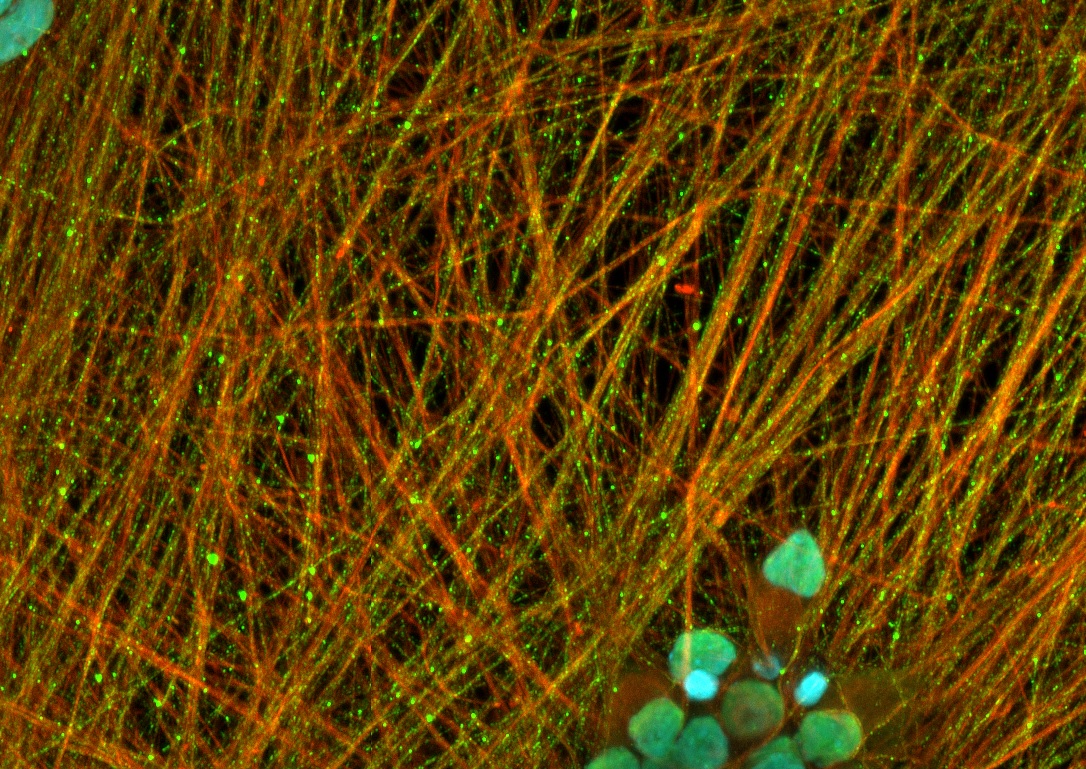
In the picture, we have stained C9orf72 human iPSC-derived motor neurons after 14 days in vitro with a TDP-43 antibody (green, nuclei with DAPI in blue, and cytoskeleton with ß-III-Tubulin in red).
Visit us at SfN meeting Nov. 12-16, 2022 in San Diego
15 June, 2022
Nov 12 at 1:00 PM
Functional Phenotypic Screening of Small Molecules in a human patient-derived cell model for Fragile X Syndrome
We developed a functional phenotypic assay with a diseased human cell line from a fragile X patient.
Cortical neurons derived from this disease cell line showed clear functional different activity patterns compared to a wild-type cell line.
We screened more than 200 compounds in this model with an MEA screen.
We identified the phosphodiesterase 10A inhibitor balipodect (TAK-063) as a potential new treatment for FXS.
We compared the potential therapeutic effects of balipodect, mavoglurant, arbaclofen, and lovastatin with this model.
Nov 16 at 8.00 AM
Functional Phenotypic Screening Models for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis with human iPSC-derived spinal motor neurons
Compared to wild-type cell lines, the hyper excitation of diseased ALS cell lines with a C9orf72 and a SOD1 mutation is shown.
The effect of astrocytes on neuronal activity was investigated.
The effects of riluzole and spermidine in these models are shown.
Nov 16 at 8:00 AM
Validation of Models for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis with human iPSC Motor-derived Neurons
Mislocalization of TDP-43 proteins in axons and dendrites is a hallmark of ALS. TDP-43 mislocalizations exist in iPSC-derived spinal motor neurons with C9orf72 mutations but not in wild-type motor neurons.
In the picture, we have stained C9orf72 human iPSC-derived motor neurons after 14 days in vitro with a TDP-43 antibody (green, nuclei with DAPI in blue, and cytoskeleton with ß-III-Tubulin in red).
C9orf72 mutant cells show increased levels of Poly(GR) dipeptides as a second hallmark.
Visit our presenter and discuss our new developments.
 infobox@neuroproof.com
infobox@neuroproof.com +49 381 54345-660
+49 381 54345-660